Flashlights have been an essential tool for centuries, from the early days of candles and oil lamps to the modern LED-powered marvels we have today. Whether you're an outdoor enthusiast, a homeowner, or just someone who appreciates the convenience of a reliable light source, understanding the different parts of a flashlight can help you make informed decisions when it comes to choosing the right one for your needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the 10 key components that make up a flashlight, providing you with a deeper understanding of how these devices work and what to look for when selecting the perfect one for your lifestyle.
A Brief History of the Flashlights
The first flashlight, or "electric hand lamp," was invented in 1899 by Joshua Lionel Cowen, the founder of the Lionel Corporation. This early device used a paper-wrapped cardboard tube, a small incandescent bulb, and a battery to create a portable light source. Over the years, flashlight technology has evolved dramatically, with advancements in battery life, light output, and overall design.
Today, flashlights come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and capabilities, catering to the diverse needs of consumers. From the compact and powerful EDC (Everyday Carry) flashlights to the rugged and high-intensity tactical models, the world of flashlights has something for everyone.

The Top Types of Flashlights You Should Know
Before we dive into the 10 parts of a flashlight, let's take a quick look at some of the most popular types of flashlights on the market:
EDC Flashlight
EDC (Everyday Carry) flashlights are small, lightweight, and designed to be carried with you on a daily basis. These compact and versatile lights are perfect for everyday tasks, such as finding your keys in the dark or illuminating your path during a power outage.
Tactical Flashlight
Tactical flashlights are built for durability and high-performance. They are often used by law enforcement, military personnel, and outdoor enthusiasts who require a reliable and powerful light source in demanding situations. Tactical flashlights typically feature a sturdy construction, a focused beam, and advanced features like strobe modes and high lumen outputs.
Diving Flashlights
Diving flashlights are specifically designed for underwater use, with waterproof and pressure-resistant housings that can withstand the challenges of the deep. These specialized lights are essential for scuba divers and underwater explorers, providing the illumination needed to navigate and observe the aquatic world.
Heavy-Duty Flashlights
Heavy-duty flashlights are built to withstand the toughest conditions, such as extreme temperatures, impacts, and exposure to the elements. These rugged lights are often used in industrial settings, construction sites, and outdoor activities where a reliable and durable light source is a must.
LED Flashlights
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) flashlights have become increasingly popular in recent years, thanks to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and impressive brightness. LED technology has revolutionized the flashlight industry, allowing for smaller, more powerful, and more versatile light sources.
Headlamp Flashlights
Headlamp flashlights are hands-free lighting solutions that are worn on the head, freeing up your hands for other tasks. These versatile lights are popular among hikers, campers, and workers who need to keep their hands free while maintaining a reliable light source.
Now that we've covered the different types of flashlights, let's dive into the 10 key parts that make up these essential tools.
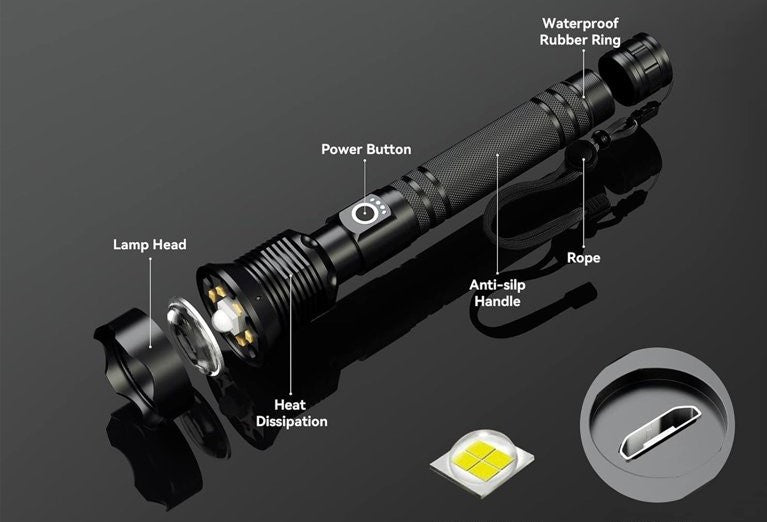
10 Parts of a Flashlight
1. Bezel
The bezel is the outer ring or housing that surrounds the lens of the flashlight. It serves several important functions, including protecting the lens from damage, providing a secure grip for the user, and in some cases, housing additional features like a strike bezel for self-defense.
2. Light Source
The light source is the heart of the flashlight, responsible for generating the illumination. Historically, flashlights used incandescent bulbs, but modern models are increasingly relying on LED (Light-Emitting Diode) technology, which offers superior brightness, efficiency, and lifespan.
3. Light Beam
The light beam is the actual output of the flashlight, the focused and directed light that illuminates your surroundings. Flashlights can produce a wide range of beam patterns, from a narrow, intense spotlight to a broader, more diffused floodlight, depending on the design and intended use of the device.

4. Reflector
The reflector is a crucial component that helps shape and focus the light beam. It is typically a parabolic or spherical surface that reflects the light from the source, creating a more concentrated and directed beam. The reflector's design and material can significantly impact the flashlight's overall performance and beam characteristics.
5. Lens
The lens is the transparent cover that sits in front of the light source and reflector. It serves to protect these sensitive components, as well as to further refine and shape the light beam. Lenses can be made from a variety of materials, such as glass or polycarbonate, and can be coated or treated to enhance their optical properties.
6. Housing
The housing is the main body of the flashlight, encasing all the internal components and providing a sturdy, protective shell. Flashlight housings can be made from a variety of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, and high-impact polymers, each offering different levels of durability, weight, and thermal management.
7. Pocket Clip
Many flashlights are equipped with a pocket clip, which allows the user to attach the light to their clothing, belt, or other gear for easy access and hands-free use. The pocket clip is a convenient feature that helps keep the flashlight secure and readily available when needed.
8. Tail Cap
The tail cap is the rear end of the flashlight, where the power switch is typically located. It serves as the interface between the user and the flashlight, allowing them to turn the light on and off, as well as access any additional features or modes.
9. Main Switch
The main switch is the primary control mechanism for the flashlight, responsible for turning the light on and off, as well as potentially cycling through different brightness levels or specialized modes. Switches can take various forms, such as push-button, twist, or sliding designs, each with its own unique feel and functionality.
10. The Circuit
The circuit is the internal electronic system that powers the light source and manages the flashlight's various functions. This includes the battery compartment, the driver that regulates the power to the LED, and any additional circuitry that enables advanced features like variable brightness, strobe modes, or battery level indicators.
Understanding these 10 key parts of a flashlight will not only help you make more informed purchasing decisions, but it will also give you a deeper appreciation for the engineering and design that goes into these versatile and indispensable tools. Whether you're an outdoor enthusiast, a DIY enthusiast, or simply someone who values the convenience of a reliable light source, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to choose the perfect flashlight for your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between a tactical flashlight and a regular flashlight?
Tactical flashlights are designed for more demanding applications, such as law enforcement, military, or outdoor activities. They typically feature a more durable construction, a focused and intense beam, and advanced features like strobe modes or high lumen outputs. Regular flashlights, on the other hand, are more suited for everyday tasks and general illumination.
How do I choose the right flashlight for my needs?
When selecting a flashlight, consider factors such as the intended use, the required brightness (measured in lumens), the beam pattern, the battery type and runtime, and the overall durability and water resistance. Determine your specific needs and then research the available options to find the best fit.
What is the difference between an LED flashlight and an incandescent flashlight?
LED (Light-Emitting Diode) flashlights are more energy-efficient, longer-lasting, and generally brighter than their incandescent counterparts. LEDs also produce less heat and are more durable. Incandescent flashlights, while less efficient, can still be a viable option for certain applications, such as providing a warmer, more diffused light.
How do I maintain and care for my flashlight?
To keep your flashlight in top condition, regularly clean the lens and reflector, replace the batteries when needed, and store the flashlight in a cool, dry place. Avoid exposing the flashlight to extreme temperatures, moisture, or physical impacts, which can damage the internal components. Consult the manufacturer's instructions for specific maintenance recommendations.
Can I use rechargeable batteries in my flashlight?
Yes, many modern flashlights are designed to work with rechargeable batteries, such as lithium-ion or NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) cells. Using rechargeable batteries can save you money in the long run and reduce waste. However, be sure to use the correct type of rechargeable battery recommended by the flashlight's manufacturer to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.